 Majority (41%) Prefer Formal Education Overall
Majority (41%) Prefer Formal Education OverallEducation has come a long way from being a privilege reserved for the elite. Now, learning opportunities are available to all through various forms of education. These mainly include formal, informal, and non-formal education.
Formal education involves structured learning in a classroom setting delivered by trained teachers. This can include primary, secondary, tertiary, and vocational education. Informal education is more optional, involving self-learning, online courses, and apprenticeships. Non-formal education is a combination of formal and informal learning, with no curriculum or syllabus, but more organized than informal learning.
Apart from this, other types of education systems include vocational, distance, alternative, global, and experimental education. Today, there are numerous options for obtaining an education, and it’s no longer exclusive to the affluent and elite.
Hence, Real Research, an online survey app, launched a survey on the types of education systems to determine the most effective education system.
Highlights:
- 66.13% have received formal education (primary, secondary, tertiary, etc.)
- 41.12% prefer formal education to other forms of education
- 18.89% consider experiential learning as effective compared to the rest
Education is an essential aspect of human life that enables individuals to acquire knowledge, skills, and values needed to live a fulfilling life. With various forms of education available, it is important to understand the types of education individuals have received. In this insight, we aim to explore the different types of education that individuals have received and which type of learning is more effective through a survey.
Our first findings indicate that a vast majority of respondents (94%) have received some form of education, while only a small percentage (6%) have not. The following sections will delve deeper into the various types of education received by the majority of respondents and explore how these types of education can impact one’s life.
Types of Education Received
In our survey on the types of education, we asked respondents about the types of education they have received. The results reveal that a significant proportion of respondents (66%) have received a formal education, which includes education provided by recognized institutions such as schools, colleges, and universities.
Another 19% of respondents reported having received informal education, which refers to learning through life experiences, self-study, and interactions with others. Additionally, 12% reported having non-formal education, which refers to structured and organized learning outside of formal institutions, such as vocational training, workshops, and online courses.
These findings suggest that while formal education is still the most common type, there are other types of learning that individuals are utilizing to acquire knowledge and skills. The following sections will provide further insight into these different types of education and their potential impacts.
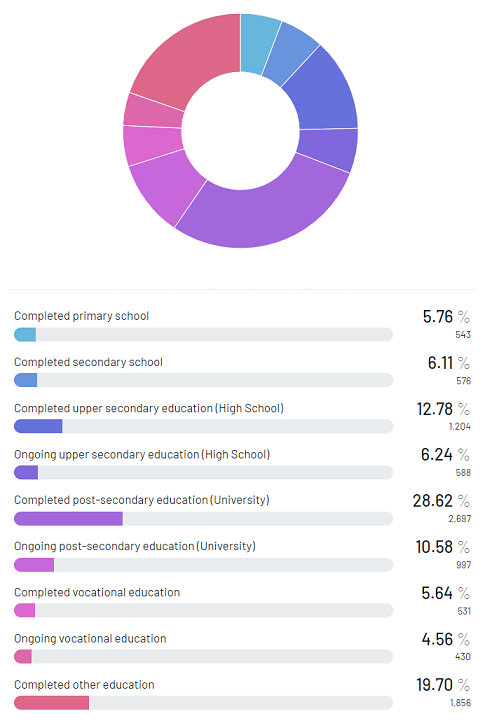
Diverse Types and Levels of Education Attained by Respondents
The following graph (figure 1) reveals the level of education respondents attained in our survey. 6% of respondents reported having completed primary school, while another 6% had completed secondary school. 13% of respondents reported having completed upper secondary education (high school), while 6% were still ongoing in high school.
Notably, a significant proportion of respondents (29%) had completed post-secondary education (university), while 11% were ongoing university studies. 6% of respondents had completed vocational education, while 5% were ongoing with vocational education. Finally, 20% of respondents reported having completed other forms of education.
Education System Preferences
Our survey on the types of education also sought to understand respondents’ preferences regarding education systems. When asked which type of education system they prefer, 41% of respondents indicated a preference for formal education, which includes education provided by recognized institutions such as schools, colleges, and universities.
15% of respondents indicated a preference for informal education, which refers to learning through life experiences, self-study, and interactions with others. 14% of respondents preferred non-formal education, which refers to structured and organized learning outside formal institutions, such as vocational training, workshops, and online courses.
Moreover, 12% of respondents preferred other types of education systems, while 18% of respondents indicated that they preferred none.
These findings suggest that while formal education remains a popular choice, a significant proportion of respondents prefer other types of education systems.
Effectiveness
In addition to preferences, the following survey reveals perceptions regarding the effectiveness of different education systems for career growth. When asked which type of education system they believe is the most effective for career growth, 26% of respondents indicated a preference for formal education, and 13% indicated a preference for informal education.
Moreover, 11% preferred non-formal education, and 29% believed that all three education systems are equally effective for career development.
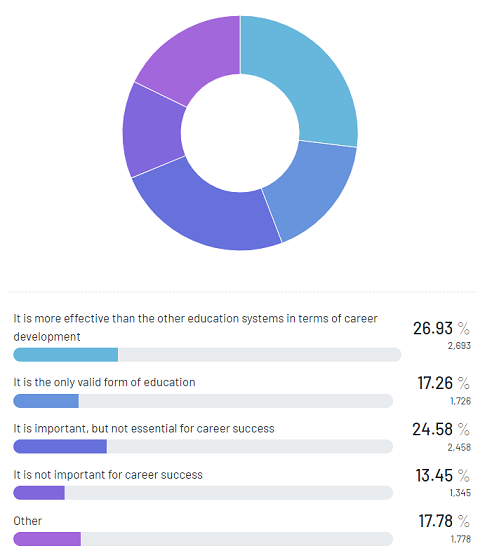
The following figure reveals respondents’ thoughts on formal education. 27% said it is more effective than the other education systems in terms of career development. Followed by 17% said it is the only valid form of education, 25% said it’s important but not as important for career success, and 13% said it’s not crucial for career growth.
However, on the other hand, when asked about informal education, 13% said it was a good substitute for formal education, 14% said it was better than all other educational systems for career development, and 12% said it was the best system overall.
Additionally, 18% of respondents said it is helpful for personal growth, followed by the statements that it is not a legitimate form of education (8%), that it is necessary but not crucial for career success (15%), and that it is not vital for career success (10%).
Similarly, 32% believe non-formal education is a more effective alternative to formal education, 29% believe it is more effective than other education systems for career development, 13% believe it is more effective than other education systems in all aspects, and 7% believe it is only effective after formal education.
Furthermore, 10% believe it is useful for personal development, 1% believe it is not a valid form of education, 3% believe it is important but not for career development, and another 1% believe it is not important for career development.
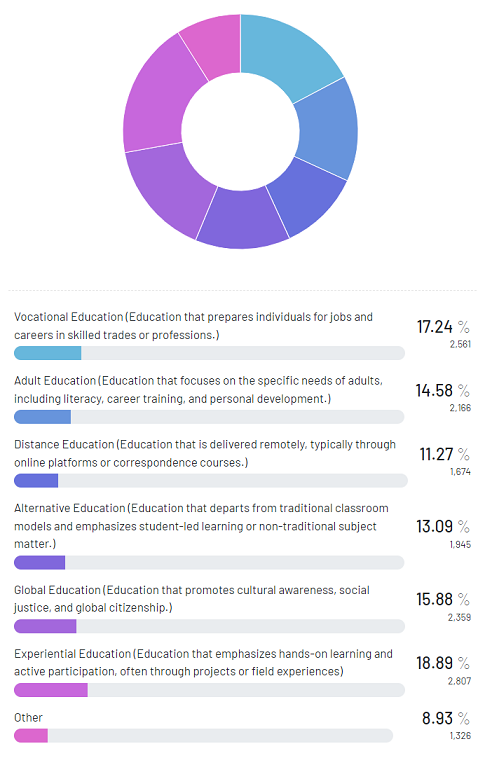
What Other Types of Education is Effective?
Our survey on the types of education also sought to understand respondents’ perceptions regarding other effective education systems. When asked which other types of education systems they consider effective, respondents provided a variety of answers. 17% of respondents stated that they consider vocational education to be effective, which refers to education and training programs that prepare individuals for specific careers.
15% of respondents said that they believe adult education to be effective, which refers to learning opportunities for adults who may not have had the opportunity to complete their education earlier in life or who wish to enhance their skills for personal or professional reasons.
11% of respondents stated that they consider distance education effective, which refers to learning opportunities delivered remotely through technology. 13% of respondents said that alternative education is effective, which refers to non-traditional forms of education that may include experiential learning, personalized instruction, and project-based learning.
Additionally, 16% of respondents stated that they consider global education effective, which refers to education promoting global citizenship and intercultural understanding. Finally, 19% of respondents said they think experiential education is effective, which refers to learning through practical experiences and hands-on activities.
These findings highlight the diverse range of education systems respondents perceive to be effective and may provide insights into potential areas for future research and development in education.
Methodology | |
| Survey Title | Survey on the Types of Education Systems |
| Duration | February 22 – March 1, 2023 |
| Number of Participants | 10,000 |
| Demographics | Males and females, aged 21 to 99 |
| Participating Countries | Afghanistan, Algeria, Angola, Argentina, Armenia, Australia, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Belarus, Benin, Bolivia,… Brazil, Brunei, Bulgaria, Burkina Faso, Cambodia, Cameroon, Canada, Chile, China, China (Hong Kong) China (Macao), China (Taiwan), Colombia, Costa Rica, Croatia, Czech Republic, Ecuador, Egypt, El Salvador, Ethiopia, Finland, France, Gambia, Georgia, Germany, Ghana, Greece, Greanada, Guatemala, Honduras, Hungary, India, Indonesia, Iraq, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Ivory Coast, Japan, Jordan, Kenya, Kuwait, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Lebanon, Libya, Lithuania, Malaysia, Maldives, Maluritania, Mexico, Moldova, Mongolia, Morocco, Mozambique, Myanmar [Burma], Namibia, Nepal, Nicaragua, Nigeria, Oman, Pakistan, Palestine, Panama, Peru, Philippines, Poland, Portugal, Qatar, Romania, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Serbia, Sierra Leone, Singapore, Slovakia, South Africa, South Korea, Spain, Sri Lanka, Tanzania, Thailand, Togo, Tunisia, Turkey, Turkmenistan, Uganda, Ukraine, United Arab Emirates, United Kingdom, United States, Uruguay, Uzbekistan, Venezuela, Vietnam, Yemen, Zimbabwe. |
RR Author
Real Research News is the media platform that presents insights and studies of wide-range of topics. It focuses on insights gathered from its survey app.







