 44.75% Are Somewhat Concerned About the Rising Healthcare Costs in the U.S.
44.75% Are Somewhat Concerned About the Rising Healthcare Costs in the U.S.A new report from PwC predicts that medical expenses in the U.S. will rise by an estimated 7% in 2024, adding to the already significant growth of over 6% in 2023 and 5.5% in 2022. Key drivers of this cost increase include the hot weight loss drug market, expensive gene therapies, and increased consolidation in hospitals and care facilities.
Employers and insurers are facing challenges with weight loss drugs, which are becoming a top drug cost for some employers. The broader health system is also experiencing inflationary pressures and worker shortages, contributing to rising costs.
These cost pressures may translate into higher insurance premiums for employers and individuals. However, there are some mitigating factors, such as more biosimilars and value-based care, which could help offset the cost burden.
Despite these efforts, the healthcare industry faces challenges in adopting innovative changes to adapt to the changing landscape. Organizations are urged to reshape strategies and invest in innovation and technology to navigate these cost challenges by 2030.
Hence, Real Research, an online survey app, launched a public opinion on the possibility of medical expenses in the U.S. Rising by 7% in 2024 to gauge the effect of the rising healthcare costs in the U.S.
Highlights:
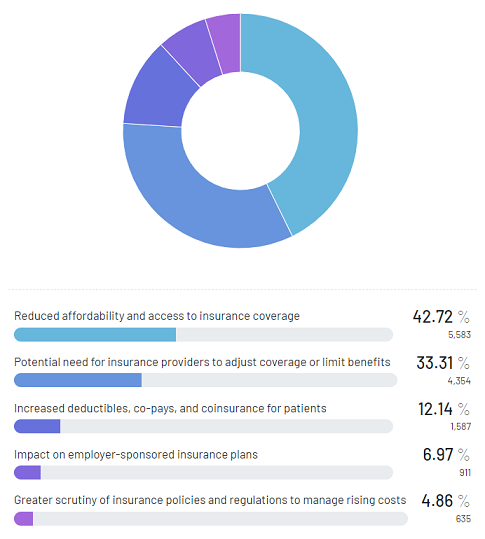
- The projected increase in patient treatment costs may result in reduced affordability and access to insurance coverage, said 42.72%.
- 29.95% believed the general public or patients might be affected the most by the rising healthcare costs in the U.S.
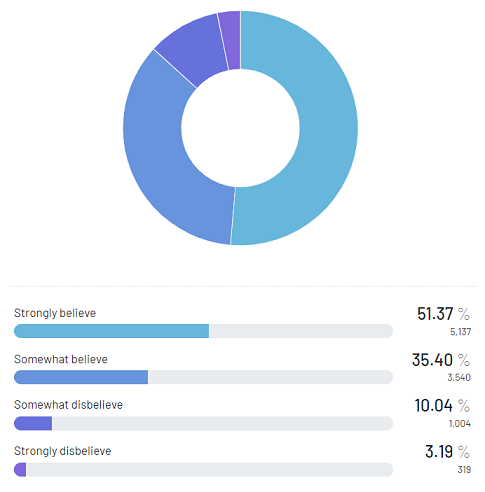
- 51.37% strongly believed patient treatment costs are rising due to inflation, rising wages, and other healthcare industry expenses.
The PricewaterhouseCoopers’ Health Research Institute’s prediction of a 7% year-over-year increase in medical costs in the U.S. for 2024 has raised significant awareness and concerns among respondents. The projected spike is higher than the trends observed in 2022 and 2023, leading to 43.91% expressing strong concern and 44.75% showing some level of concern.
Meanwhile, 9.25% were not so concerned about the rising cost of healthcare in the United States, and 2.09% were not concerned at all.
The anticipation of U.S. hospitals and physicians seeking higher rate increases in contract negotiations has prompted nearly 90% of respondents to believe that this surge will impact the overall healthcare services sector worldwide.
As for the effects of rising healthcare costs, respondents identified potential financial burdens on individuals and families (39.11%) and higher insurance premiums and out-of-pocket expenses (26.16%) as significant concerns. Reduced access to healthcare services (21.6%), growing healthcare inequality, and disparities (10.51%) were also noted concerns.
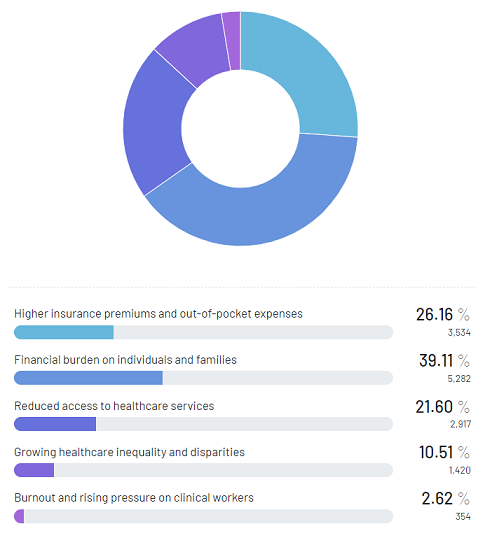
Concerns Over Projected Patient Treatment Cost Increase: Affordability, Insurance Coverage, and Deductibles
When we asked about the impacts of the rising healthcare costs in the U.S., respondents expected that the projected increase in patient treatment costs would lead to reduced affordability and access to insurance coverage (42.72%). There are concerns regarding insurance providers potentially adjusting coverage or limiting benefits (33.31%) and the possibility of increased deductibles, co-pays, and coinsurance for patients (12.14%).
Who Will Be Most Impacted by Rising Healthcare Costs
In terms of the parties most impacted by rising healthcare costs, the general public or patients were specified by 29.95%, followed by hospitals and healthcare facilities (16.62%), insurance companies (16.22%), pharmaceutical companies (14.19%), and government healthcare programs and budgets (23.02%).
The report’s assertion that rising healthcare costs are driven by high inflation, rising wages, workforce shortages, and other expenses was strongly supported by 51.37% of respondents. A significant portion (35.4%) also believed in the accuracy of the reasons behind the projected increase. On the other hand, 10.04% had doubts about the findings and 3.19% did not believe at all.
Overall, the data highlights the heightened awareness and concern surrounding the possibility of medical expenses rising by 7% in 2024, reflecting the significance of the issue and the potential implications for various stakeholders within the healthcare ecosystem.
Methodology | |
| Survey Title | Public Opinion on the Possibility of Medical Expenses in the U.S. Rising by 7% in 2024 |
| Duration | July 13, 2023 – July 20, 2023 |
| Number of Participants | 10,000 |
| Demographics | Males and females, aged 21 to 99 |
| Participating Countries | Afghanistan, Algeria, Angola, Argentina, Armenia, Australia, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Belarus, Benin, Bolivia,… Brazil, Brunei, Bulgaria, Burkina Faso, Cambodia, Cameroon, Canada, Chile, China, China (Hong Kong) China (Macao), China (Taiwan), Colombia, Costa Rica, Croatia, Czech Republic, Ecuador, Egypt, El Salvador, Ethiopia, Finland, France, Gambia, Georgia, Germany, Ghana, Greece, Greanada, Guatemala, Honduras, Hungary, India, Indonesia, Iraq, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Ivory Coast, Japan, Jordan, Kenya, Kuwait, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Lebanon, Libya, Lithuania, Malaysia, Maldives, Maluritania, Mexico, Moldova, Mongolia, Morocco, Mozambique, Myanmar [Burma], Namibia, Nepal, Nicaragua, Nigeria, Oman, Pakistan, Palestine, Panama, Peru, Philippines, Poland, Portugal, Qatar, Romania, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Serbia, Sierra Leone, Singapore, Slovakia, South Africa, South Korea, Spain, Sri Lanka, Tanzania, Thailand, Togo, Tunisia, Turkey, Turkmenistan, Uganda, Ukraine, United Arab Emirates, United Kingdom, United States, Uruguay, Uzbekistan, Venezuela, Vietnam, Yemen, Zimbabwe. |
RR Author
Real Research News is the media platform that presents insights and studies of wide-range of topics. It focuses on insights gathered from its survey app.







